Staffordshire Bull Terriers, known for their loyal and energetic nature, are wonderful companions but may sometimes face certain health problems. Behind their adorable, muscular build, they can occasionally encounter joint issues, skin conditions, and hereditary diseases.
Of course, these problems may not occur in every dog, but being aware of them and taking preventive measures through early diagnosis can help ensure they lead a healthy and happy life. Let’s take a closer look at these common health issues to provide the best care for your beloved companion!
İçerik Tablosu
The Most Common Health Problems in Staffordshire Bull Terriers
1. Hip Dysplasia
Hip dysplasia is a common genetic orthopedic issue seen in Staffordshire Bull Terriers. This condition begins with excessive looseness in the hip joints of affected dogs. The looseness disrupts the proper contact between the femur and the hip socket, leading to misalignment over time. This misalignment causes the joint surfaces to rub against each other, resulting in wear and tear. Consequently, inflammation and painful arthritis can develop in the dog’s joints.
Dogs with hip dysplasia typically start showing symptoms between 6 and 12 months of age. During this period, your dog may experience difficulty walking, noticeable limping after exercise, or stiffness in movement. These symptoms often become more pronounced after physical activity. A veterinarian may observe reduced flexibility and tenderness in the affected hip. In such cases, an X-ray is usually required for a definitive diagnosis.
For treatment, most symptoms can be alleviated with rest and pain relief medications. However, in severe cases, physical therapy, specialized diets, or surgical interventions may be necessary.
2. Skin Allergies
Staffordshire Bull Terriers are genetically predisposed to skin allergies, meaning their immune system tends to overreact to certain environmental substances such as pollen, dust, or chemicals. The breed’s genetic makeup makes them more susceptible to these allergic reactions.
Allergic reactions are triggered when the immune system improperly responds to common substances like pollen, dust, chemicals, or certain foods. During this reaction, the immune system releases inflammatory chemicals under the skin, causing intense itching. When your dog starts scratching excessively to relieve the itch, it can damage the skin, creating an entry point for secondary infections.
The most commonly affected areas include the abdomen, armpits, paws, and ears. Most Staffordshire Bull Terriers begin showing these symptoms between 1 and 3 years of age.
Treatment for allergic reactions typically includes anti-inflammatory medications, specialized shampoos, and effective parasite control methods. If secondary skin infections develop, antibiotics may be required. In cases of suspected food allergies, veterinarians often conduct dietary trials, eliminating specific foods to identify the allergen causing the reaction.
3. Mitral Valve Disease (MVD)
Mitral valve disease is a common heart condition, particularly in older dogs. This disease involves the degeneration of the heart’s mitral valve, leading to blood leaking backward into the heart. This makes it difficult for the heart to pump sufficient blood to the body, gradually putting extra strain on the heart.
The symptoms of mitral valve disease typically include:
- Dry cough: A recurring dry cough, often observed after waking up or during periods of rest.
- Exercise intolerance: Your usually energetic dog may tire quickly during walks or stop playing sooner than usual.
- Weakness and fatigue: A lack of enthusiasm for daily activities and an increased tendency to sleep.
- Breathing difficulties: Struggled breathing or deep, labored breaths.
- Heart failure: Advanced cases may exhibit signs of heart failure.

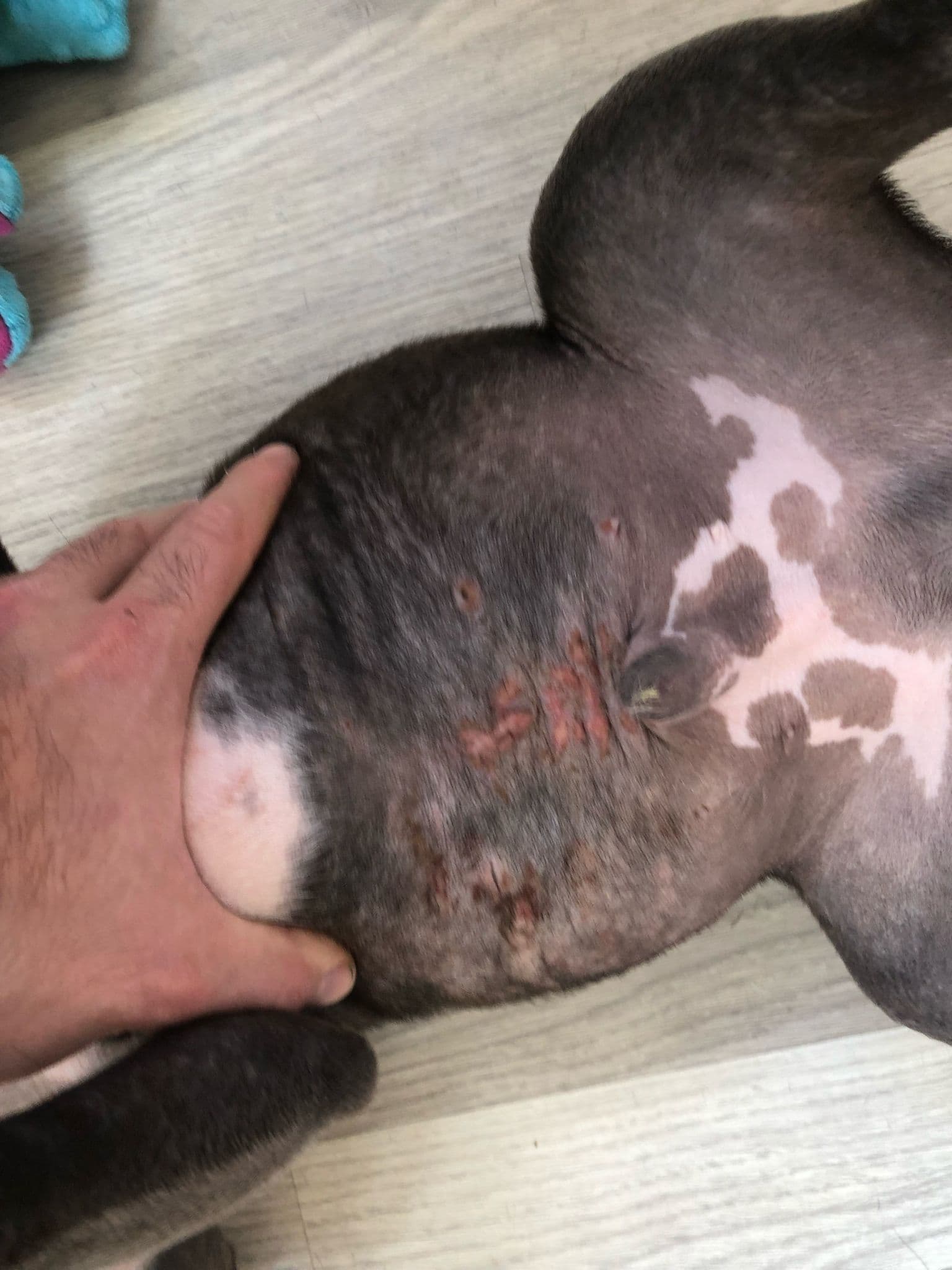
Colour Dilution Alopecia (CDA)
Colour dilution alopecia (CDA) is a genetic skin condition commonly seen in dogs with diluted coat colors, such as blue or other light shades. This condition results from a mutation in the genes that determine coat color. The mutation causes irregular pigment cell accumulation, leading to compromised skin and coat health. Breeds like the Staffordshire Bull Terrier with blue or diluted coats are at higher risk of developing this disease.
Symptoms of CDA include:
- Hair loss: Typically begins on the dog’s back, head, and sides, spreading over time with significant hair shedding.
- Brittle coat: The dog’s fur becomes weak, thinner, and more prone to breakage.
- Skin infections: Areas of hair loss are more prone to infections and inflammation.
- Itching and irritation: Dryness, redness, persistent itching, and irritation of the skin may occur.
Unfortunately, there is no definitive cure for this genetic condition. However, symptoms can be managed effectively. Veterinarians often recommend specialized shampoos, moisturizing creams, and dietary supplements to maintain skin health and provide relief for your dog. Regular skin care and a balanced diet can also help mitigate the effects of the disease.
For more detailed information, feel free to read our blog by clicking here.
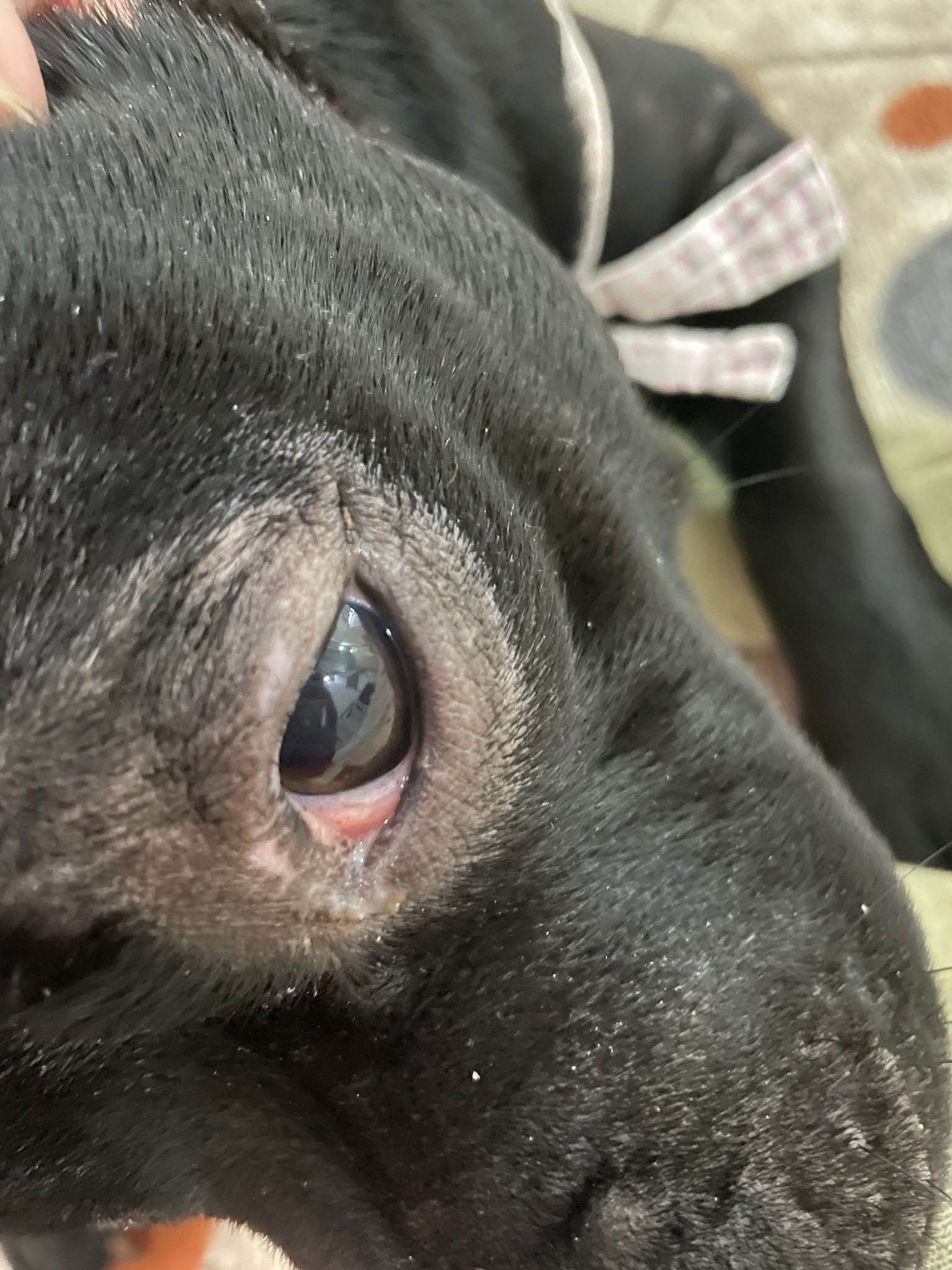
5. Cataracts
Cataracts occur when opacities develop in the lens of the eye, causing it to appear cloudy. This condition obstructs the passage of light through the lens, leading to symptoms of vision loss in dogs. Common signs in dogs with cataracts include bumping into objects and poor vision, especially in low light.
There are two main causes of cataracts:
- Hereditary cataracts: In some dogs, cataracts are genetically inherited and can appear a few months after birth. In such cases, dogs may face a high risk of complete blindness by the age of two or three.
- Age-related or secondary cataracts: These can develop spontaneously in older dogs or as a result of other conditions such as diabetes or glaucoma.
Cataract surgery is a highly successful treatment option for many cases. However, some dogs can adapt remarkably well to vision loss and continue living a normal life even without surgery. Post-surgery recovery is usually positive, and your dog’s vision can be significantly restored. For a definitive diagnosis and treatment plan, it’s essential to have your dog examined by a veterinarian.
How Can We Prevent It?
Genetic Testing
Many common diseases in dogs are genetic and can be prevented by carefully screening animals before breeding. Genetic testing and responsible breeding practices are essential to ensure a healthy future generation.
This process may include X-rays of the dog’s elbows and hips or DNA testing to detect genetic conditions such as Colour Dilution Alopecia or hereditary cataracts. Through genetic testing, dogs with serious hereditary conditions can be excluded from breeding programs, preventing the transmission of these diseases to future generations.
For this reason, choosing a responsible breeder who follows a careful breeding policy and is transparent about the health and genetic history of their dogs is crucial. Ensure your breeder can provide documentation on the health status and genetic history of their dogs. Responsible breeders take the necessary steps to safeguard the health of both your dog and future generations.
2. Weight Management
For dogs born with elbow or hip dysplasia, effective management of these conditions largely depends on maintaining good weight control and limiting strenuous exercise. Excess weight increases the strain on the joints, worsening joint disorders and accelerating the onset of arthritis as the dog ages.
To strengthen your dog’s joints without overloading them, opt for shorter, more frequent walks instead of long walks or strenuous activities. For example, avoid high-impact activities like running or playing fetch, which place excessive stress on the joints. Instead, focus on light exercises that support joint health and improve endurance.
3. Regular Coat Care
Regular grooming and bathing of your dog can make a significant difference in managing allergic skin conditions. In addition to maintaining skin and coat health, keeping your home free from airborne allergens such as dust and debris is equally important.
Frequent brushing and bathing help remove dead skin cells, dust, and dirt from your dog’s coat, reducing the risk of irritation and allergic reactions. Additionally, using appropriate moisturizing shampoos can help hydrate your dog’s skin and alleviate allergic symptoms.
4. Early Diagnosis
Identifying symptoms early allows your veterinarian to perform necessary tests and start treatment promptly. This can make it easier to control diseases before they progress and significantly improve your dog’s quality of life.
Do not ignore subtle signs such as behavioral changes, loss of appetite, decreased energy, deterioration in skin and coat health, or cloudiness in the eyes. Paying attention to these early warning signs can help prevent more serious issues in the future. Regular veterinary check-ups and adhering to recommended vaccination schedules are crucial steps in safeguarding your dog’s health.


Most Read Articles
Hypothyroidism in Dogs: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Methods
In this blog post, we’ll talk about hypothyroidism, a prevalent health concern in dogs. We...
May
Fungal Infections in Dogs: Symptoms and Psychological Effects
Fungal infections in dogs can have a serious influence on their health. In this post,...
Sep
Nosebleeds in Dogs: 12 Causes and What You Can Do
ebleeds in dogs can cause concern for their owners. In this post, we’ll look at...
Oct