Dermatomycosis, a common and contagious skin disease in dogs, is caused by fungal infections. In this post, we will look at what dermatomycosis is, what problems it can cause, what its symptoms are, how to diagnose it, what treatment options are offered, and whether it spreads to humans.
İçerik Tablosu
What is Dermatomycosis?
Dermatomycosis is a condition in dogs that results from fungal infections on the skin. It is caused by fungi called “dermatophytes,” which infect the skin, hair, and nails.
These fungi thrive in warm and moist environments, and they are most commonly found in dogs with weakened immune systems or those living in unhygienic conditions. The most frequent fungal infections in dogs include Microsporum canis, Microsporum gypseum, and Trichophyton mentagrophytes.
Dermatomycosis is highly contagious and can spread from infected dogs to other animals and even humans, making early diagnosis and treatment crucial.
What Diseases Can Dermatomycosis Cause?
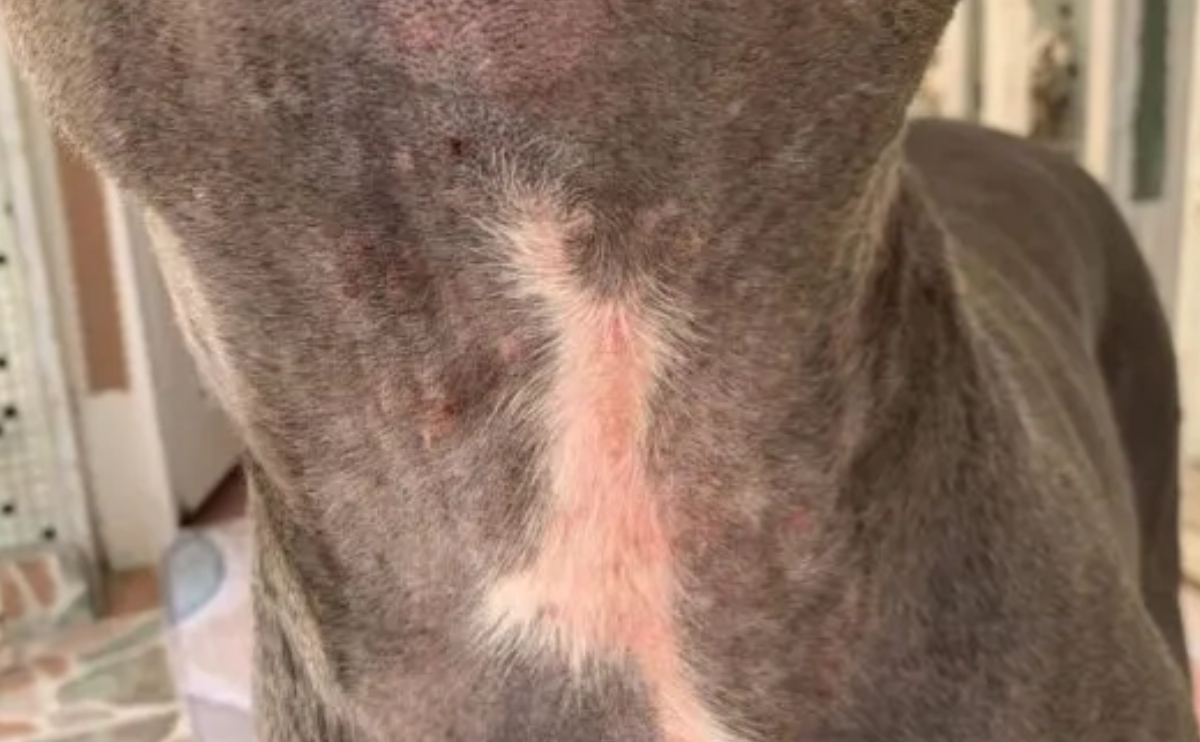
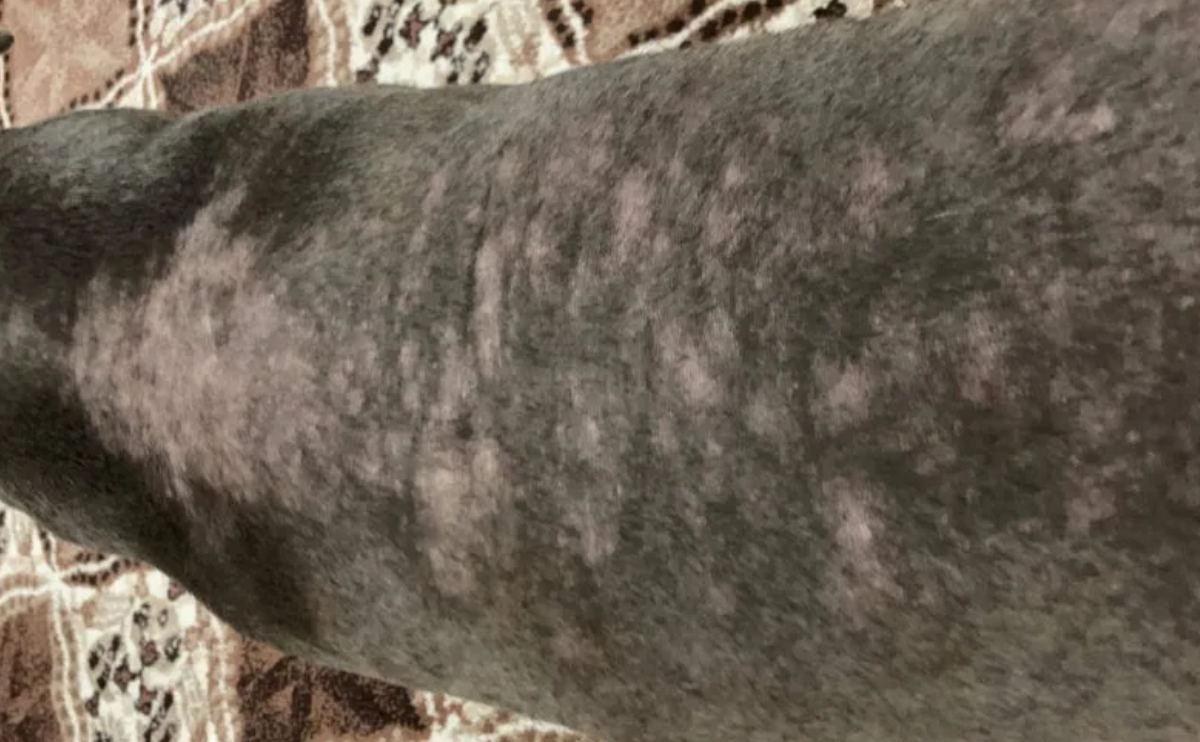
Dermatomycosis can cause a variety of skin diseases in dogs. The most common manifestation is “ringworm” (tinea), which causes circular, scaly sores. As the infection spreads, vast portions of the skin may get affected, resulting in severe itching, redness, and hair loss.
Secondary bacterial infections may also develop, complicating the condition further. In some cases, dogs may experience chronic dermatitis and skin ulcers.
Left untreated, dermatomycosis can negatively impact a dog’s overall health and quality of life, potentially causing severe complications. This fungal infection can also trigger conditions like Alopecia, which leads to hair loss.
What Are the Symptoms of Dermatomycosis?
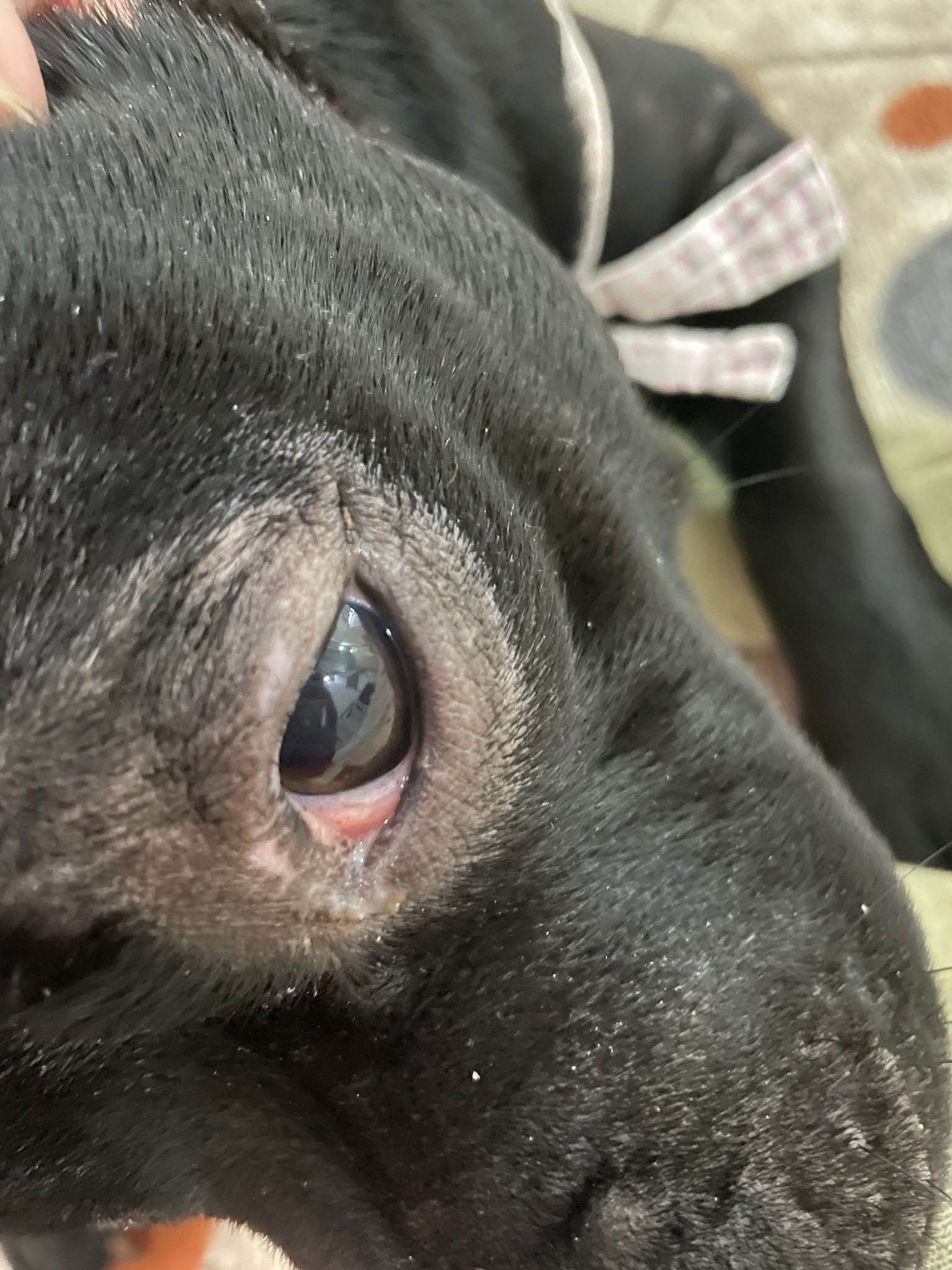
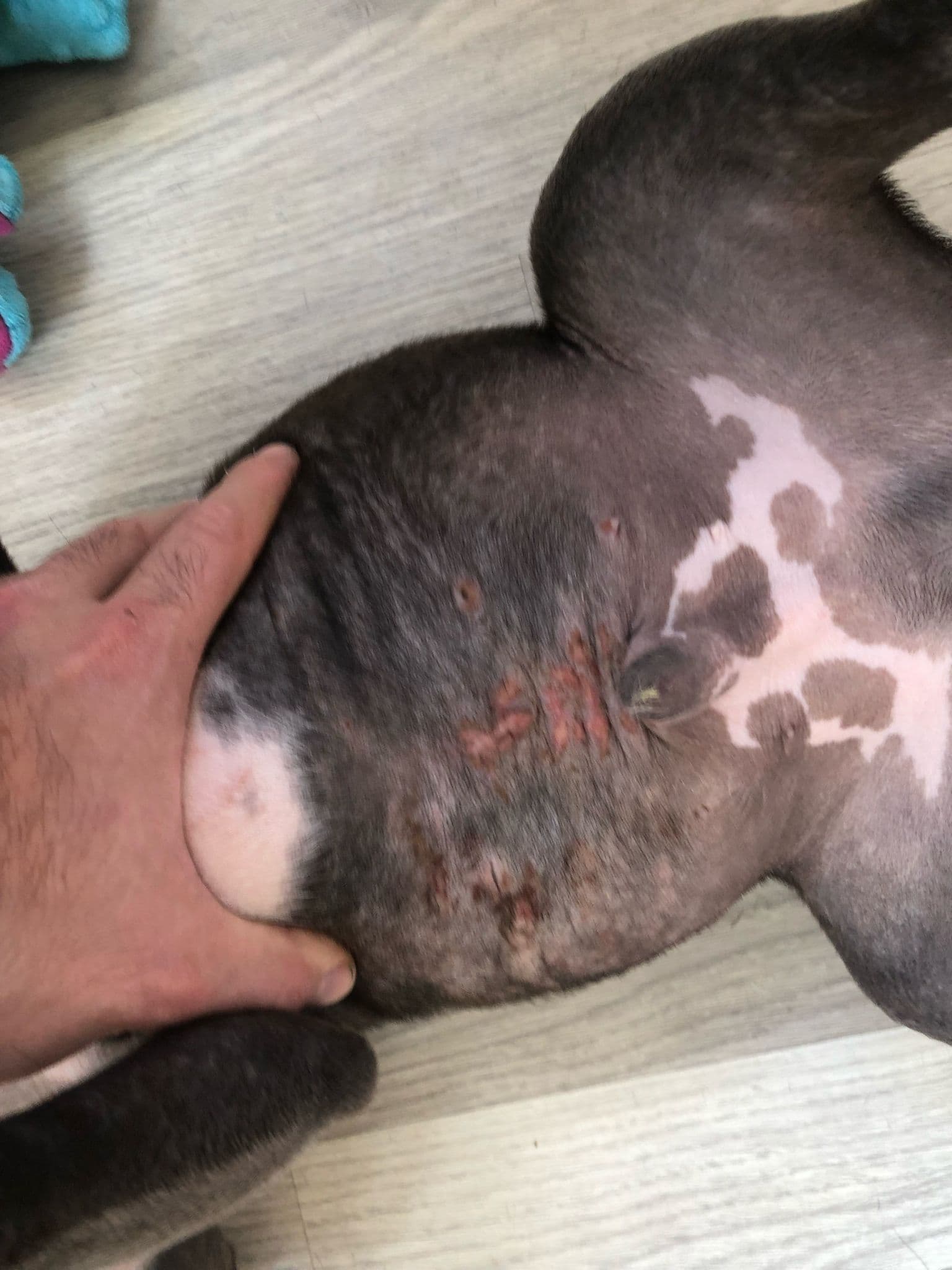
Dermatomycosis symptoms in dogs frequently manifest as major skin changes. Lesions often form on the head, ears, legs, and body. Hair loss occurs in the affected areas, which frequently appear scaly and flaky. Some dogs may exhibit no symptoms at all, which makes diagnosis more difficult. Common symptoms include:
- Hair Loss: Infected areas experience hair loss, often taking on a circular appearance.
- Round and Red Lesions: Circular, red lesions form on the skin in infected areas.
- Crusting Skin: The infected areas may develop crusting and flakiness.
- Itching: The infected regions can be itchy, causing the dog to scratch continuously, which can spread the infection.
- Secondary Infections: Wounds caused by scratching can lead to bacterial infections.
How is Dermatomycosis Diagnosed?
A veterinarian will usually do a physical examination and laboratory tests to diagnose dermatomycosis. The veterinarian may collect hair and skin samples from the afflicted regions for examination under a microscope. Additionally, fungal culture tests and examinations with a Wood’s lamp can aid in diagnosis. A Wood’s lamp is a specialized UV light that detects fungal diseases. In some circumstances, a biopsy may be required. Early diagnosis is critical for preventing the spread of the infection and initiating appropriate treatment.
How is Dermatomycosis Treated?
Dermatomycosis in dogs is typically treated with antifungal drugs, which can be administered topically (to the skin) as well as systemically (orally). Antifungal shampoos, lotions, and sprays are common topical therapies, whilst antifungal tablets and capsules are used systemically. Common drugs include:
- Itraconazole: An oral antifungal that works by affecting the fungal cell membrane, inhibiting the growth of the fungus.
- Ketoconazole: Available for both topical and oral use, this medication is effective in treating fungal infections.
- Miconazole: Another topical antifungal that reduces the effects of the fungus on the skin.
- Griseofulvin: A systemic antifungal commonly used to treat dermatophyte infections.
The duration of treatment varies depending on the severity and extent of the illness, and might range from several weeks to a few months. Additionally, keeping the atmosphere clean and disinfected is critical to the treatment’s success. Always consult with your veterinarian before using any medication or cream.
Can Dermatomycosis Spread to Humans?
Yes, dermatomycosis in dogs can spread to people. This is referred to as a zoonotic infection. Direct contact with an infected dog can lead to fungal diseases in people.
Children, the elderly, and people with compromised immune systems are among those most at risk. In humans, the infection may cause itchy, red, and scaly skin sores.
As a result, when treating an infected dog, it is critical to observe stringent hygiene procedures and take personal precautions.


Most Read Articles
Nosebleeds in Dogs: 12 Causes and What You Can Do
ebleeds in dogs can cause concern for their owners. In this post, we’ll look at...
Oct
Ways to Socialize Staffordshire Bull Terrier Puppy
English Staff puppies are known for their tenacity, bravery, and strong affection for people. Proper...
Sep
How to Stop Your English Staff Puppy Chewing Things
English Staffies can be wonderful family companions due to their loving and loyal nature. This...
Nov